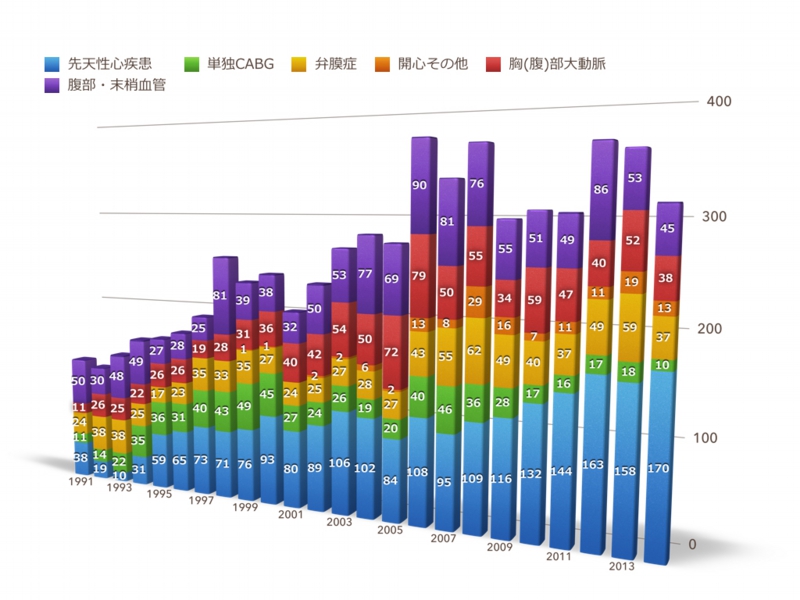
Number of surgeries performed
手術総数の推移
Surgery of the large arteries
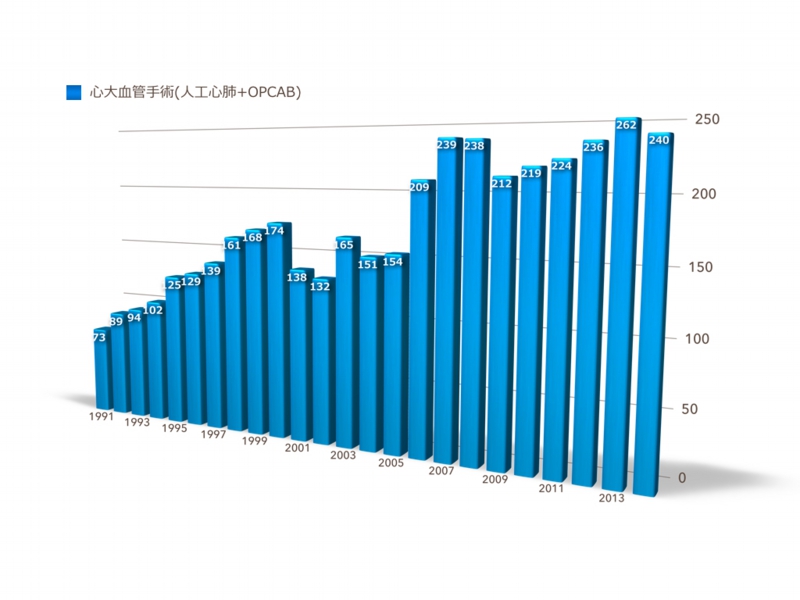
Adult cardiac surgery
Ischemic heart disease
The treatment of angina or heart attacks caused by narrowed or blocked vessels that nourish the heart is normally done by inserting a catheter through the vessel. However, it became apparent that for the improvement effect on prognosis, heart surgery (coronary artery bypass) is a better course of action.
In Japan, in order to reduce patient burden, coronary artery bypass is more commonly performed while the heart is beating (off-pump surgery) than when the heart beat has been stopped by medication (under cardiac arrest; on-pump surgery). However, recently it was reported that better surgical results were obtained under cardiac arrest using an artificial heart-lung machine. Therefore, surgery under cardiac arrest is also a recognized option. The same method cannot be applied to every patient, however. Recently, the number of patients who require a coronary artery bypass while having an underlying medical condition, including diabetes, renal failure, stroke and others, has been increasing. We assess each patient’s condition and select the best method—surgery using an artificial heart-lung machine or beating heart surgery, in order to obtain the best results for the patient.
Coronary artery bypass
Valvular disease surgery
It is difficult to treat valvular diseases medically and thus, the ultimate solution is surgery. In this case, prosthetic replacement, valve replacement with an artificial valve, or valvuloplasty, repair using the patient’s own valve, is performed.
In the case of “stenosis”, the valve becomes hard; therefore, prosthetic replacement is the primary treatment method. Depending upon the patient’s age and medical background, we select either a biological valve or an artificial valve. In the case of “regurgitation”, valvuloplasty is our primary method. Although not all valves can be repaired, valvuloplasty has been successfully executed on most patients in our department. Although performing a valvuloplasty on the aortic valve is difficult, we are progressively using this method for our younger patients.
In the case of infectious endocarditis with valve infection, depending upon the level of infection, sometimes it is difficult to preserve the original tissue and a prosthetic replacement must be used. However, we try to perform valvuloplasty while preserving the original valve to the greatest extent possible.
Aortic surgery
Blood vessel prosthesis implantation
When the wall of the aorta, which carries blood from the heart, becomes weak, blood pressure causes it to expand. This is called an aortic aneurysm.
An aortic aneurysm will rupture if it continues to expand and once this occurs, it is fatal. Aortic aneurysms cannot be treated by conventional medicine; the primary method of treatment is replacement of the vessel with an artificial vessel (blood vessel prosthesis implantation). It is a high-risk extended surgery with heavy bleeding and requires complex techniques. Although surgical results have improved with the progression of medicine, it nonetheless remains a risky surgery, with loss of life of the patient a possibility. Therefore, a decision on the treatment of an aortic aneurysm is made after comparing the risk of observation with the risk of surgery.
In our department, we have been performing blood vessel prosthesis implantation to treat aortic diseases such as aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection. We perform blood vessel prosthesis implantation not only for the aortic arch and abdominal aorta but also more complex targets such as the aortic root and the thoracoabdominal aorta.
In order to perform surgery more safely and with less bleeding, we are implementing the use of various devices.
Blood vessel prosthesis implantation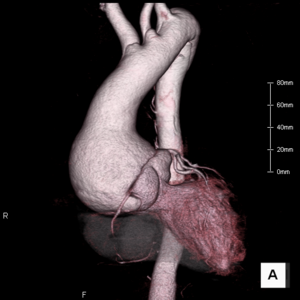
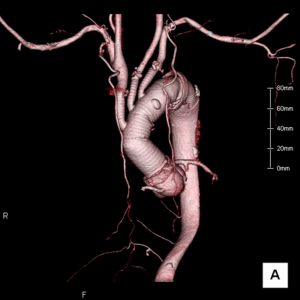
Stent graft
In our hospital, stent graft treatment for aortic aneurysm is performed in a hybrid operating room.
Stent graft treatment confers less burden to the body and is thus is a friendlier treatment method for the patient. However, with regard to radical cure, it is less effective compared to blood vessel prosthesis implantation. Therefore, careful consideration is necessary prior to its implementation. The treatment cannot be performed unless anatomical conditions are met. Therefore, this treatment method is not for everyone. We assess each patient’s condition to determine which method is better—stent graft or blood vessel prosthesis implantation—and then propose the treatment plan to the patient.
図)Hybrid Operating Room
Pediatric cardiac surgery
Time to consider patient QOL (quality of life)
The condition in which a problem exists in the shape or function of the heart at birth is called congenital heart disease. Due to progress in diagnostic and surgical methods as well as in maintenance pre- and post-surgery, the success rate for surgery has greatly improved. Also, due to progress in both medical and surgical treatments, the numbers of patients who receive surgery during childhood and grow to adulthood as well as and patients with adult congenital heart disease who are diagnosed only after becoming adults are increasing.
Septal defect
In our department, the primary surgical method for patients weighing 8-30kg is right posterolateral thoracotomy (with an opening of 7-12cm around the right scapula such that the scar is invisible from the front). Other methods are determined through consultation with the patient. We believe that it is possible to perform surgery on patients weighing less than 6kg without a blood transfusion. The surgery itself takes 2-3 hours and the post-surgery hospital stay is 6-9 days.
Ventricular septal defect
Since such defects close naturally in many cases, patients are observed very carefully. In case of patients with heart failure symptoms (difficulty in breathing, unable to ingest milk or gain weight) or high lung blood pressure, surgery may be required for patients at the neonate/infant age group. If aortic insufficiency is caused by turbulent flow, the surgery is necessary in order to stop the symptoms from advancing. This surgery requires a skin incision of 3-8cm in the center of the chest. The surgery itself requires 1-2 hours, with a post-surgery hospital stay of about 1-2 weeks.
Neonate open heart surgery
Some congenital heart diseases such as complete transposition of the great vessels, total anomalous pulmonary venous connection and coarctation of the aorta complex require surgery under cardiac arrest using an artificial heart lung machine for neonates. In Japan, more than 400 patients receive surgery each year using an artificial heart lung machine. In our department, we perform this type of surgery on about 20 patients per year.
Surgery for functional single ventricle
With single ventricle, only one ventricle pumps blood to the lungs and entire body. Therefore, the blood is mixture of venous blood (black colored blood with less oxygen) and arterial blood (red-colored blood with abundant oxygen), which causes cyanosis (purple lips and nails) as well as heart failure in patients. Total cavopulmonary connection (TCPC) operation and the Bidirectional Glenn procedure are procedures that allow one functional ventricle to perform the role of left ventricle by directing blood flow to the lungs, which is the role of the right ventricle under normal conditions, through venous blood pressure. TCPC operation is conducted in a stepwise manner. In the majority of cases, pulmonary artery banding or a systemic-to-pulmonary artery shunt is executed at birth in order to control for heart failure. Surgeries for reconstruction of the aortic root and aortic arch such as the Norwood procedure and the Damus-Kaye-Stansel (DSK) procedure previously used to have low success rates, but we are now able to perform them more safely. The next step of the surgical treatment is a Bidirectional Glenn procedure, which makes the blood return from the upper body and flow directly into the lungs. This is done when the patient is between 2-6 months old. Since blood returning from the lower body travels to the entire body from the ventricle without going through the lung, cyanosis cannot be eliminated; however, heart failure occurrence is reduced. Later on, many patients receive a TCPC operation to improve cyanosis. Since veins of the lower body are connected to the pulmonary artery using an artificial valve, almost all veins are directly connected to the pulmonary artery and thus, cyanosis is eliminated.
Adult congenital heart diseases
We are performing the Bentall procedure, reconstruction of the right ventricular outflow tract, and closure of a residual shunt on patients with problems with the aortic root or right ventricular outflow tract following surgery for Tetralogy of Fallot or surgery for complete transposition of the great vessels. We also perform Valve-sparing aortic root replacement surgery for enlarged aortic root accompanying Marfan syndrome and the outcome is excellent.
Tricuspid valve replacement and cardiac resynchronization therapy are used for treatment of corrected transposition of the great vessels and some patients are on the waiting list for heart transplantation.
The TPCP conversion procedure is often applied to patients who have received the Fontan procedure. Often, patients with arrhythmia and cirrhosis have problems during surgery. However, treatment of such patients is improving through the implementation of pre- and post-surgery procedures such as diagnosis and treatment using a catheter in the Pediatric Department and evaluation of liver function by the Department of Gastrointestinal Medicine.
Serious heart failure
Ventricular reduction
In patients with serious heart failure, the left ventricle of the heart is significantly expanded with reduced contractive force akin to a stretched out balloon.
Although the only treatment method for terminal heart disease is heart transplantation, this option is not for everyone since there are not enough heart donors.
We are one of few institutions that conducts ventricular reduction procedures to repair and improve the patient’s own heart. We have reported numerous research results, including those from nation-wide multi-center research.
We serve as a secretariat for the “Research Group on Surgery for Serious Heart Failure” which is a nation-wide research group which manages a registry data base.
Overlapping cardiac volume reduction operation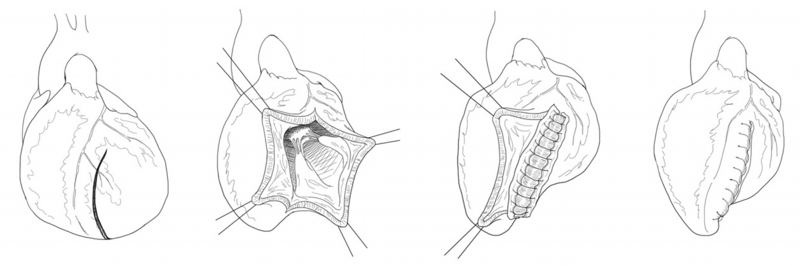
Ventricular assist device and heart transplantation
Our hospital is the only “heart transplantation facility” and “implantable ventricular assist device operating facility” in Hokkaido. In 2004, we performed the second heart plantation in Hokkaido, which was our long-cherished wish.
We formed a heart team consisting of various departments and members in various occupations including cardiovascular surgeons, cardiologists, and transplantation coordinators. Once a week, we hold a conference to discuss about patients who have been referred to us by various medical facilities in Hokkaido.
図)A snapshot of the heart team conference
![]()
New procedures
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement is a new treatment method for aortic stenosis, which replaces the aortic valve with an artificial valve by inserting a catheter from the blood vessel at the base of the foot or from the tip of the heart. It is a minimally invasive procedure compared to traditionally conducted open heart surgery and has become popular in Europe and the US. Recently, transcatheter aortic valve replacement was accepted in Japan and our hospital was approved for the procedure in July, 2014. Our interdisciplinary heart team (Department of Cardiovascular Medicine and our department) is currently preparing for the implementation of this procedure. At this point, the procedure is only applicable for high-risk patients such as the elderly. Depending upon the condition of the patient and fine standard of the valve structure, it may not be applicable for certain patients. However, there are high expectations for this procedure as a minimally invasive treatment for valvular heart diseases.
Minimally invasive heart surgery
Minimally invasive heart surgery results in less pain and a quicker recovery in addition to having significant cosmetic merit. However, heart surgery conducted from a small incision requires a high level of skill and experience, and sometimes necessary adjustments must be carefully considered due to complications from the procedure, which are different than those of regular heart surgery. The Adult Cardiovascular Surgery Group in our department performs minimally invasive heart surgery mainly consisting of right small thoracotomy for adult septal defect, mitral insufficiency, tricuspid valve insufficiency and benign cardiac tumor.
Laser treatment of varicose veins
Laser treatment is a new treatment method for varicose veins that can be performed under local anesthesia and it is possible to be discharged on the same day the procedure is conducted. Unlike past procedures (stripping procedure) which removes the veins, this method burns and closes the vein from the inside of the vessel by insertion of a catheter through the vein from the skin. Depending upon the location of vein reflux, laser treatment may not be possible, however. Please consult a physician when you visit us.


